Brain Health Scan
Brain Health Scan
Couldn't load pickup availability
Share
Description
This is an advanced brain health examination aimed at those who want to go the extra mile to optimize their brain health. We analyze over 162 data points related to your brain using quantitative MRI (qMRI), screen for 53 different brain diseases, and compile the results in a personalized report with concrete advice for further improvement. The examination is suitable for those who are healthy today, with no signs of pathology linked to dementia or Alzheimer's, but who wish to be proactive in improving the physiological structure of their brain.
To ensure that you can truly trust the examination to deliver the benefits you are looking for, our method is based on scientifically substantiated analyses and advanced qMRI technology. You will receive personalised and tailored feedback that makes the results both concrete and measurable. We collaborate with specialist neurologists, which provides high credibility and expert support. In addition, we offer the option of regular follow-ups so that you can monitor your brain health over time and clearly see any improvements.
It is beneficial to have the examination done regularly to create points of comparison, as soon as one month after your first examination. The MRI examination does not involve any radiation and is therefore completely safe to repeat often. A good time to have the examination done is in connection with your birthday, to ensure that your brain has not aged faster than you have.
The report
The report is compiled by a specialist neurologist and also includes a tailored action plan with concrete strategies for improving your brain health. You will receive clear recommendations on how you should exercise and eat, as well as additional measures you can take to strengthen your brain health in a way that can be measured over time. If necessary, advice is also given on the type of medical follow-up that is recommended. An example report can be found here.
Here's how to proceed
1. Order your examination
Add the examination to your shopping cart and pay using your preferred method.
2. Select your date
After placing your order, you will receive an email where you can select the date and time for the scan. Your ID number ensures a secure IT environment for your data.
3. Fill in the health questionnaire
Fill in a secure form with questions about your health and lifestyle.
4. Magnetic camera examination (10 minutes)
The examination itself is performed in a magnetic camera and takes only 10 minutes.
5. We create your report
Our specialist neurologist reviews and compiles their assessment in an individual written report that you receive digitally via a secure link.
This includes
Volumetric measurements (162)
Standard volumes (91)
Accumbens area volume (total)
Amygdala volume (total)
Angular gyrus – volume (total)
Anterior cingulate gyrus – volume (total)
Anterior orbital gyrus – volume (total)
Anterolateral temporal lobe volume (total)
Basal forebrain – volume (total)
Banks of the superior temporal sulcus – volume (total)
Caudal anterior cingulate gyrus – volume (total)
Caudatus volume (total)
Choroid plexus – volume (total)
CSF-normalized volume (total)
Cerebral gray matter – volume (total)
Cerebral white matter – volume (total)
Cerebellar cortex volume (total)
Cerebellar white matter volume (total)
Cerebellum (combined GM + WM) – volume (total)
Cerebellar vermis lobulus I–V – volume (total)
Cerebellar vermis lobulus VI–VII – volume (total)
Cerebellar vermis lobulus VIII–X – volume (total)
Cerebellar vermis (total) – volume (total)
Cerebral cortex volume (total)
Corpus callosum volume (total)
Cuneus – volume (total)
Dorsolateral prefrontal volume (total)
Entorhinal area volume (total)
Frontal lobe volume (total)
Frontal operculum – volume (total)
Frontal pole – volume (total)
Anterior insula volume (total)
Fusiform gyrus – volume (total)
Globus pallidus – volume (total)
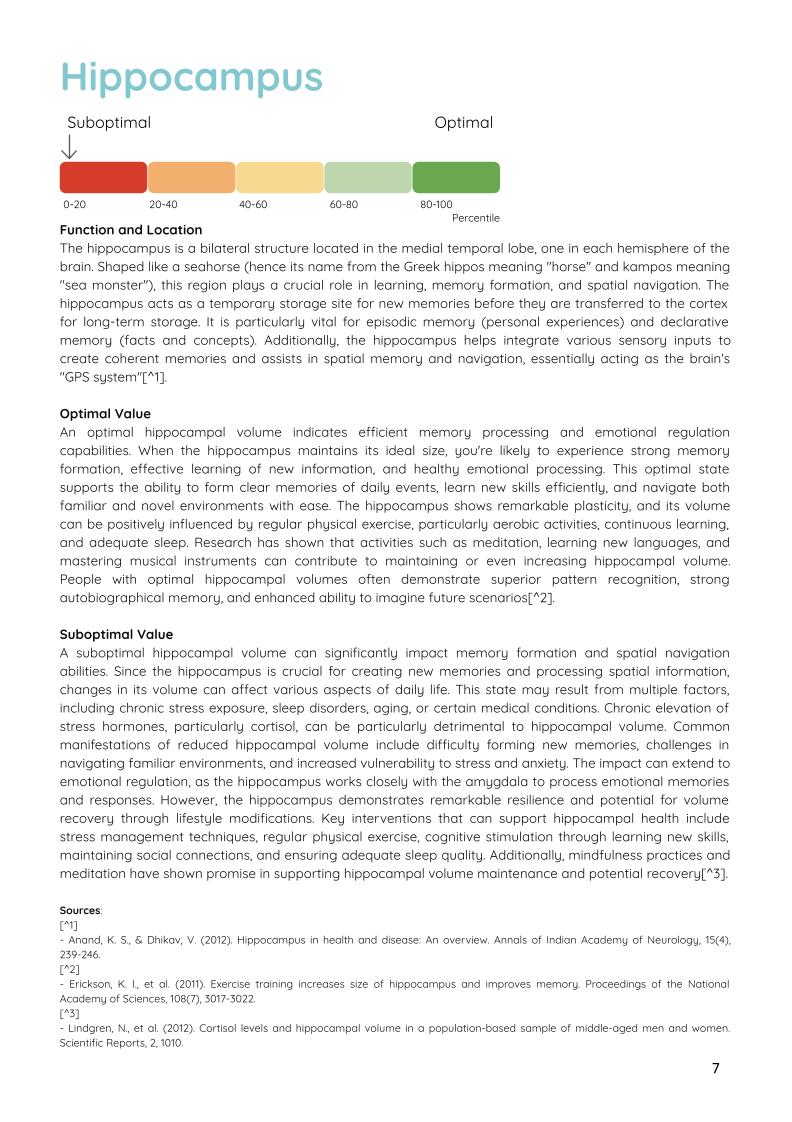
Hippocampus – volume (total)
Brain parenchyma volume (total)
Brain stem volume (total)
Pituitary gland – volume (total)
Hypothalamus – volume (total)
Inferior frontal gyrus – volume (total)
Inferior lateral ventricle volume (total)
Inferior occipital gyrus – volume (total)
Inferior parietal lobule – volume (total)
Inferior temporal gyrus – volume (total)
Insula volume (total)
Isthmus cingulate – volume (total)
Lateral ventricle volume (total)
Lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) – volume (total)
Lateral occipital cortex – volume (total)
Lateral orbitofrontal gyrus – volume (total)
Lingual gyrus – volume (total)
Medial geniculate nucleus (MGN) – volume (total)
Medial orbitofrontal gyrus – volume (total)
Mesencephalon tegmentum – volume (total)
Middle frontal gyrus – volume (total)
Middle occipital gyrus – volume (total)
Middle temporal gyrus – volume (total)
Midbrain (mesencephalon) – volume (total)
Nucleus accumbens – volume (total)
Occipital lobe volume (total)
Paracentral lobule – volume (total)
Parahippocampal gyrus – volume (total)
Parietal lobe volume (total)
Pars opercularis (part of inferior frontal gyrus) – volume (total)
Pars orbitalis (part of inferior frontal gyrus)
Pars triangularis (part of inferior frontal gyrus) – volume (total)
Pericalcarina cortex – volume (total)
Planum polare – volume (total)
Planum temporale – volume (total)
Pontina tegmentum – volume (total)
Pons – volume (total)
Postcentral gyrus – volume (total)
Posterior cingulate gyrus – volume (total)
Precuneus – volume (total)
Precentral gyrus – volume (total)
Primary auditory cortex – volume (total)
Primary motor cortex – volume (total)
Primary somatosensory cortex – volume (total)
Primary visual cortex – volume (total)
Putamen – volume (total)
Rostral anterior cingulate – volume (total)
Rostral middle frontal gyrus – volume (total)
Spinocerebellum (lobules I–V) – volume (total)
Superior frontal gyrus – volume (total)
Superior occipital gyrus – volume (total)
Superior parietal lobule – volume (total)
Superior temporal gyrus – volume (total)
Supramarginal gyrus – volume (total)
Pineal gland (epiphysis) – volume (total)
Temporal fusiform cortex – volume (total)
Temporal poles – volume (total)
Thalamus – volume (total)
Transverse temporal gyrus – volume (total)
Ventral diencephalon – volume (total)
Third ventricle volume (total)
Fourth ventricle volume (total)
WMH volumes (5)
Brain tissue WMH volume (total)
Periventricular WMH volume (total)
Juxtacortical WMH volume (total)
Deep white matter WMH volume (total)
Infratentorial WMH volume (total)
T1 Hypointense Volumes (5)
Brain Tissue T1 Hypointense Volume (total)
Periventricular T1 Hypointense Volume (total)
Juxtacortical T1 Hypointense Volume (total)
Deep White Matter T1 Hypointense Volume (total)
Infratentorial T1 hypointense volume (total)
TBI lesion volumes (4)
Corpus callosum TBI lesion volume (total)
Lobar white matter TBI lesion volume (total)
Cerebellum TBI lesion volume (total)
Brain stem TBI lesion volume (total)
Lesion-related measurements (35)
Total number of lesions, volume, and change are reported for:
Brain tissue
Periventricular
Juxtacortical
Deep white matter
Infratentorial
Atrophy indices (6)
Medial Temporal Lobe Atrophy (MTA)
Global Cortical Atrophy (GCA) Cerebral cortex
Global Cortical Atrophy (GCA) Frontal lobe
Global Cortical Atrophy (GCA) Temporal lobe
Global Cortical Atrophy (GCA) Parietal lobe
Global Cortical Atrophy (GCA) Occipital lobe
Surface & Asymmetry (8)
Midbrain area
Pons area
Midbrain/pons area ratio
Midbrain area (3 sections)
Pons area (3 sections)
Midbrain/pons area ratio (3 sections)
Hippocampus asymmetry score
Cerebral gray/white matter asymmetry score
Other indices (8)
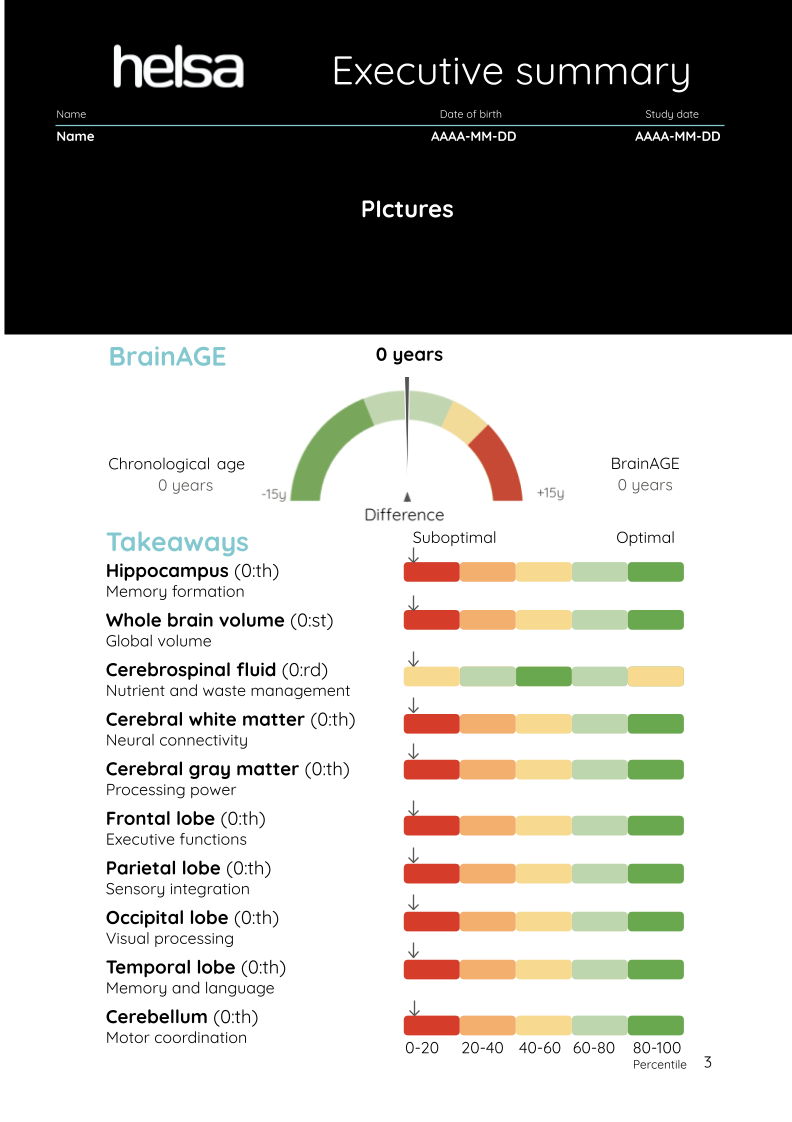
Chronological brain age
Estimated brain age (BrainAGE)
Relative brain age (BrainAGE gap/BAG)
Global estimated Fazekas (total)
Estimated callosal angle
Scaling factor for head size
Midbrain/pons volume ratio
Midbrain/pons area/volume ratio
Over 45
If you are over 45 years old, we will also provide a probability assessment of whether you are: Cognitively normal, Alzheimer's, Frontotemporal dementia, or Vascular dementia.
The volumetric data points not shown in the sample report will be shared in a .csv file.
Also included in the report
Lifestyle analysis
Exercise
Sleep
Diet
Depression
Work
Neuroradiological review
A specialist in neuroradiology will manually review the images taken in the MRI scanner. The following 53 diseases can be detected by the neuroradiologist, and follow-up with and without contrast may be required for better resolution in some cases.
Tumors & tumor-like lesions
High- and low-grade gliomas
Meningiomas (mainly larger/bulky)
Metastases ≥ 3 mm with edema or mass effect
Vestibular/other cranial nerve schwannomas
Pituitary macroadenomas, craniopharyngiomas
Epidermoid and dermoid cysts, lipoma
Pineal cyst (≥ 1 cm causes shape change)
Demyelinating & white matter disease
Multiple sclerosis (plaques in periventricular, juxtacortical, infratentorial zones)
ADEM and other acute inflammatory myelins
Small vessel disease/leukoaraiosis (hypertensive, vascular dementia)
Leukodystrophies (e.g., CADASIL, metachromatic)
Vascular & hemorrhagic
Subacute intracranial hemorrhage (methemoglobin T1-bright)
Chronic lacunar infarcts, encephalomalacia
Venous/cortical infarcts with edema
Major contusions, post-traumatic gliosis (small aneurysms, AVM, and recent ischemia require MRA/DWI/SWI)
Infection & inflammation
Encephalitis (HSV, autoimmune) with cortical/medial temporal edema
Abscess/cerebrite stages (ring shape later requires contrast)
“Dirty CSF” in purulent meningitis or early subarachnoid hemorrhage
Degenerative & epileptogenic
Hippocampal sclerosis
Cortical atrophy in Alzheimer's, FTD, cerebellar degeneration
Normal pressure hydrocephalus pattern (Evans index, DESH signs)
Congenital malformations
Corpus callosum agenesis/dysgenesis, Chiari I/II
Lissencephaly, polymicrogyria, focal cortical dysplasia
Dandy-Walker, holoprosencephaly, arachnoid cyst
Syringomyelia, tethered cord
Hydrocephalus & cyst/CSF-related
Obstructive/communicating hydrocephalus
Aqueduct stenosis, foramen Monro blockage
Porencephaly, post-ischemic glial scar cyst
Spinal cord & spinal structures (in covered volume)
Disc herniation, spinal stenosis, degenerative changes
Intramedullary tumors (ependymoma, astrocytoma), extradural meningioma/schwannoma
Demyelinating plaques in the spinal cord